The Best Fluffy Pancakes recipe you will fall in love with. Full of tips and tricks to help you make the best pancakes.
Body Composition: Explain the Difference Between Essential Body Fat and Storage Body Fat
Have you ever wondered what your body fat percentage really means? Or why some fat is considered essential while other types can pose health risks? Understanding body composition goes beyond just numbers on a scale; it’s about learning how your body stores and utilizes fat and the critical roles these fats play in overall health.
Table of Contents
ToggleIn this blog, we’ll break down the Explain the difference between essential body fat and storage body fat, highlighting their unique functions and why both matter for your well-being. Essential body fat, as the name suggests, is vital for survival, protecting organs and regulating key bodily processes. On the other hand, the storage of body fat serves as an energy reserve but, in excess, can lead to health complications. Whether you’re on a fitness journey or simply want to better understand your body, this guide will provide you with the insights you need to make informed decisions. Let’s dive into the science behind body composition and discover how you can strike the right balance for a healthier you!
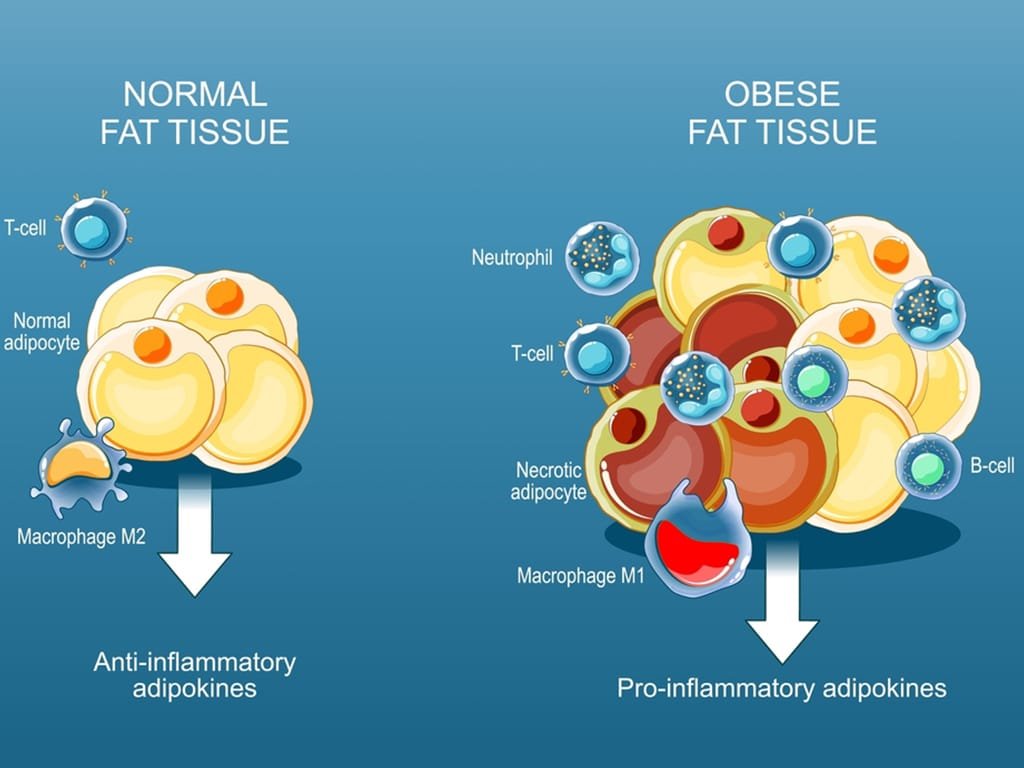
Key Takeaways
- ‘Essential body fat’ is critical for fundamental bodily functions.
- ‘Storage body fat’ acts as an energy reserve, impacting your overall health.
- Understanding both ‘types of fat’ can help you make informed health choices.
- Maintaining a balance between essential and storage of ‘body fat’ is vital.
- Awareness of ‘body fat’ types aids in effective weight management strategies.
Understanding Body Composition
Body composition is key to your health. It’s about the mix of fat, muscle, bone, and other tissues in your body. Knowing how fat works is important for a healthy life.
Essential ‘fat and storage’ fat is needed for important body functions. It helps make hormones, keeps body temperature right, and helps absorb nutrients. is like a backup energy source for your body.
The Role of Fat in the Body
Fat does many important things for your health. These include:
- Keeping your body warm
- Protecting important organs
- Helping your body use vitamins A, D, E, and K
- Storing energy for when you need it
Types of Fat and Their Functions
Fat comes in different types, each with its own job:
| Type of Fat | Function | Health Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Essential Fat | Supports cellular function and hormone production | Vital for overall health and bodily functions |
| Storage Fat | Provides energy reserves for the body | Excess accumulation can lead to health issues |
Knowing about the different fats and their roles helps you improve your body composition. It guides you in making better choices for your health and lifestyle.
What is Essential Body Fat?
Essential body fat is key for your health, making up the least amount needed for good function. Men usually need 2-5% of their body weight in fat, while women need 10-13%. This fat protects organs, helps with hormone balance, and supports metabolism.
Importance of Essential Fat for Health
The role of essential fat is huge. It acts as a shield for your organs, keeping them safe from harm. It’s also vital for making hormones, which affect your mood and how fast you burn calories. Essential fat helps with absorbing nutrients and keeping energy levels balanced.
Sources of Essential Body Fat
To keep essential ‘body fat’ healthy, eat foods rich in good fats. Here are some great options:
- Nuts – Full of unsaturated fats and packed with nutrients.
- Avocados – Rich in healthy fats and fiber, boosting heart health.
- Fatty fish – Salmon and mackerel are full of omega-3s.
- Seeds – Chia and flaxseeds are good for fats and protein.
Adding these foods to your diet can help you stay healthy. They ensure your body gets the nutrients it needs to function at its best.
What is Storage Body Fat?
Storage ‘body fat’ is a key part of your body’s makeup. It acts as a backup energy source when you don’t eat enough. Knowing how it builds up and what it does is important for staying healthy.
How Storage Fat Accumulates
Storage fat builds up when you eat more calories than you burn. This extra energy turns into fat and is stored in your body’s fat cells. Several things can make you store more fat, like:
- Eating too many processed foods.
- Not being active enough.
- Your genes play a role.
- Imbalances in hormones that affect fat storage.
Functions of Storage Fat in the Body
Storage fat is vital for your health. It does several important jobs, including:
- Supplying energy when you’re fasting or very active.
- Keeping your body temperature stable by insulating it.
- Acting as a shock absorber for your organs.
- Helping make hormones that control many body functions.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Reserve | Storage fat gives you energy when you’re not eating or exercising. |
| Insulation | It keeps your body warm by preventing heat loss. |
| Cushioning | It protects your organs and tissues from injury. |
| Hormonal Regulation | It helps make hormones like estrogen and leptin. |
In the right amount, storage of ‘body fat’ is good for you. It helps with energy and other body functions. But too much can cause health problems. Knowing your fat levels and making healthy choices can greatly improve your health.
Explain the Difference Between Essential Body Fat and Storage Body Fat
It’s important to know the difference between essential ‘body fat’ and storage ‘body fat’. Each type has its own role in your health. They have different functions and can affect your health in different ways.
Physiological Differences
Essential ‘body fat’ is needed for important body functions like hormone production and keeping your body warm. It’s found in organs, bones, and the central nervous system. On the other hand, the storage of ‘body fat’ is mainly for energy storage. It’s found under the skin and around organs, but too much can be a problem.
Health Implications
Having too much excessive storage fat can lead to serious health issues. It can cause obesity, which raises the risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and high blood pressure. Knowing this highlights why it’s key to keep the right balance of both fat types for good health.

The More About Body Fat Percentage
Knowing your ‘body fat’ percentage is key to checking your health and fitness. There are many ways to measure body fat. Knowing the right essential fat percentages helps you set realistic fitness goals.
How to Measure Body Fat Percentage
To get an accurate body fat reading, you can use several methods. Here are a few:
- Skinfold Calipers: These calipers pinch the skin at different spots to guess body fat.
- Bioelectrical Impedance: This method sends electrical signals to figure out body composition. It gives a quick body-fat percentage estimate.
- Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA): Seen as one of the most precise, DEXA scans use X-rays to split fat from lean mass.
Ideal Body Fat Percentages
Ideal ‘body fat’ percentages change with age, gender, and how active you are. Here’s a general guide:
| Category | Men (%) | Women (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Essential Fat | 2-5 | 10-13 |
| Athletes | 6-13 | 14-20 |
| Fitness | 14-17 | 21-24 |
| Acceptable | 18-24 | 25-31 |
| Obesity | 25+ | 32+ |
Knowing your ideal ‘body fat percentages’ helps you tailor your workout plan.
The Various Types of Body Fat
Knowing about the different ‘types of fat’ in your body is key to understanding health risks. ‘Subcutaneous fat’ and visceral fat are two types that are very important. They have unique features and effects on health.
Subcutaneous Fat vs. Visceral Fat
is right under your skin. It feels soft and can be pinched. It helps protect your body and keeps you warm.
Visceral fat, on the other hand, is deep in your belly. It wraps around important organs like the liver and heart. Too much of this fat can lead to serious health problems.
Impacts of Different Fat Types on Health
The effects of fat types on health are different. ‘Subcutaneous fat’ is not as harmful. But, too much visceral fat can increase the risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
Knowing this helps you make better choices for your health and weight.
| Type of Fat | Location | Health Risks | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subcutaneous Fat | Just beneath the skin | Lower health risks | Cushions and insulates the body |
| Visceral Fat | Surrounding internal organs | Higher health risks (e.g., heart disease) | Plays a role in hormone regulation |
Fat Distribution and Its Importance
Knowing how fat is spread in your body is key to your health. ‘Fat distribution’ shows where and how body fat is important stored. It affects your health in many ways. Understanding this can help spot health risks tied to different fat patterns.
Understanding Fat Distribution in the Body
Body fat doesn’t spread evenly. Some people have fat around their belly, while others have it in their hips and thighs. This matters a lot because it’s linked to health risks.
For instance, those with more belly fat face higher risks of heart disease and metabolic problems. But, those with fat in their hips and thighs are generally at lower storage risk for heart issues.
- Visceral Fat: Located around internal organs, this type is associated with more severe health risks.
- Subcutaneous Fat: Found beneath the skin, this type typically poses fewer health concerns.
- Risk Factors: Understanding your ‘fat distribution’ can help identify risk factors that need addressing.
Monitoring your ‘fat distribution’ is essential for spotting health risks. This knowledge helps you make better health choices. It leads to better ways to stay healthy and well.
How Body Mass Index Relates to Body Fat
Understanding the link between body mass index (BMI) and essential body fat is necessary key to knowing your health. BMI is a tool used to see if your weight is healthy based on your height and weight. It’s important to know what BMI measures and its limits.
What BMI Measures Related to Fat
BMI calculates a number based on your weight and height. It sorts people into weight categories like underweight, normal, overweight, and obese. These categories show health risks from too much body fat. But, BMI doesn’t tell the difference between muscle and fat, leading to wrong ideas about your body.
Limitations of BMI in Evaluating Body Fat
BMI has big limits when checking body fat. It doesn’t consider muscle, bone density, or fat placement. People with more muscle might be seen as overweight or obese, even with low body fat. Also, BMI doesn’t show where fat is, which is key for health risks. Knowing these limits helps you find better ways to check your body and health.
Maintaining a Healthy Body Fat Level
To keep a ‘healthy body’ fat level, you need to understand many factors. These include what you eat, how active you are, your genes, and your lifestyle. Knowing these can help you manage your body’s composition better.
Factors Influencing Body Fat Levels
Your ‘body fat percentage’ isn’t just about diet or exercise. Many things affect how much fat you have, such as:
- Genetics: Your genes play a big role in how your body handles fat.
- Diet: Eating whole foods helps keep body fat healthy, while processed foods can cause it to rise.
- Physical Activity: Working out regularly helps burn fat and keep muscles strong.
- Lifestyle Choices: Getting enough sleep, managing stress, and staying hydrated are all important for body fat control.
Strategies for Healthy Body Composition
There are effective ways to improve your body fat levels. Here are a few:
- Set Realistic Goals: Having reachable fitness goals helps keep you motivated and track your progress.
- Incorporate Variety in Exercise: Doing both cardio and strength training helps burn fat better.
- Monitor Your Diet: Keeping a food diary or using apps helps ensure you’re getting the right nutrients.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water helps your metabolism and overall health.
| Factor | Impact on Body Fat |
|---|---|
| Genetics | Affects fat distribution and storage capabilities. |
| Diet | Influences caloric intake and nutritional quality. |
| Physical Activity | Boosts metabolism and helps burn calories. |
| Lifestyle | Impacts hormonal balance and stress levels. |
The Health Risks of Excess Body Fat
Too much body fat, or Fat storage, is a big health worry. Knowing the risks can help you make better choices. It’s not just about looks; it affects your health deeply.
Impact of Storage Body Fat on Health
Too much ‘storage fat’ can cause serious health problems. Studies show it increases the risk of:
- Heart disease
- Type 2 diabetes
- Certain cancers
- Hypertension
- Sleep apnea
It’s important to know these risks. It can motivate you to make healthier choices.
Preventative Measures to Reduce Health Risks
There are ways to lower these risks. Here are some steps:
- Do at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise a week.
- Eat a balanced diet with fruits, veggies, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Check your body weight and composition often.
- Drink plenty of water and avoid too much sugar and fat.
- Get help from doctors to make a health plan that’s right for you.
By taking these steps, you can control your health and lessen the effects of ‘storage fat’.

Conclusion
It’s important to know the ‘difference between essential body fat’ and storage ‘body fat’ for your health. Essential ‘body fat’ helps with hormone production, keeps you warm, and protects your organs. On the other hand, ‘storage body fat’ is the extra fat that builds up when you eat more calories than you burn.
Knowing about these types of ‘body fat’ helps you make better choices in your life. It’s key to managing your ‘body fat’ to stay healthy. By focusing on ‘healthy body’ composition, you can avoid serious health problems linked to too much storage of ‘body fat’.
Staying informed about ‘body fat’ types and their health effects is vital. As you learn more about ‘body fat’, remember the difference between essential and ‘storage fat’. This knowledge will help you make choices that lead to a healthier life.
FAQ
What is the ‘difference between essential body fat’ and storage body fat?
Essential ‘body fat’ is the minimum needed for your body to function work right. It makes up about 2-5% of a man’s weight and 10-13% of a woman’s. Storage ‘body fat’, on the other hand, builds up when you eat more than you burn. It acts as energy storage.
Why is essential body fat important for health?
Essential body fat protects your organs, controls hormones, and helps with metabolism. It also helps absorb nutrients and keep your body warm. This makes it key to your health.
How does storage body fat accumulate in the body?
Storage body fat grows when you eat more than you burn. Bad eating habits and not moving much can cause it to build up over time.
What are the health risks associated with excess storage of body fat?
Too much storage of total body fat can lead to heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. It can also harm your heart and body shape.
How can I measure my ‘body fat percentage’?
You can measure ‘body fat percentage’ with skinfold calipers, bioelectrical impedance, or DEXA scans. These methods give a better idea of your body composition than just weight.
What is the ideal ‘body fat percentage’ for men and women?
The ideal body-fat percentage varies by age, gender, and activity level. For men, it’s 10-20%, and for women, 18-28%. Staying within these ranges can improve your health.
What are subcutaneous fat and visceral fat?
is under your skin, while visceral fat is around your organs. While ‘subcutaneous fat’ is mostly harmless, too much visceral fat is risky for health, like diabetes and heart disease.
Why is ‘fat distribution’ important for health?
Where fat is stored matters a lot for your health. For example, more visceral fat, like in an apple-shaped body, is riskier than ‘subcutaneous fat’, like in a pear-shaped body.
How does Body Mass Index (BMI) relate to body fat?
BMI uses height and weight to estimate body fat. But it’s not perfect because it can’t tell muscle from fat. This can lead to wrong body composition assessments.
What strategies can help maintain a healthy body fat level?
To keep a ‘healthy body’ fat level, eat a balanced diet with good fats, exercise regularly, and avoid processed foods. Setting achievable fitness goals and tracking your progress can also help improve your body shape.
What preventative measures can reduce health risks from excess body fat?
To lower body fat health risks from too much body fat, stay active, eat well, and get regular health checks. These steps are key to managing body fat and reducing obesity-related risks.



